What Is Cold Plasma Technology?
Cold Plasma Technology (also known as Non-Thermal Plasma or Low-Temperature Plasma) is a state of matter where a gas is partially ionized, generating a unique mix of reactive species without significantly heating the bulk gas. Here's a breakdown:
-
Core Concept:
-
Plasma is often called the "fourth state of matter" (beyond solid, liquid, gas). It consists of ions, free electrons, neutral atoms/molecules, and various excited species.
-
In thermal/hot plasma (like in welding arcs or lightning), all particles (electrons, ions, neutrals) are in near thermal equilibrium at very high temperatures (thousands of °C).
-
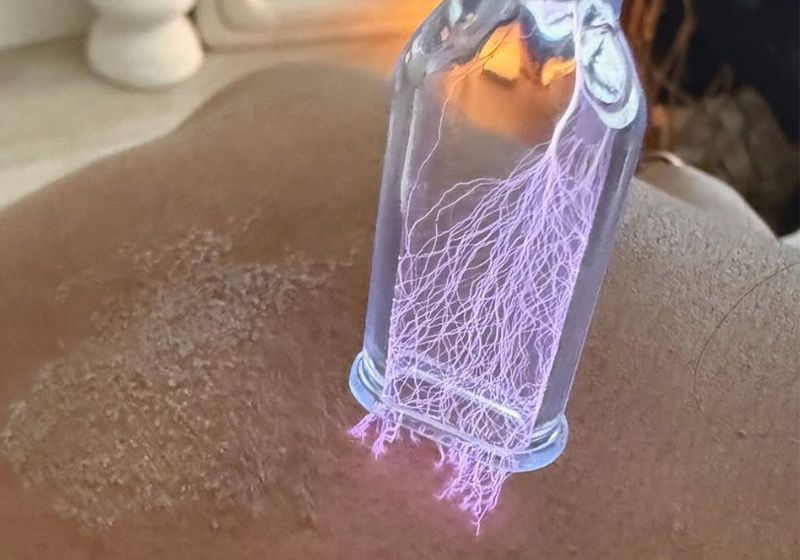
Cold plasma achieves a non-equilibrium state. Electrons are highly energized (10,000-100,000+ °C equivalent), but the heavier ions and neutral gas molecules remain close to room temperature (typically 25-60°C). This is key.
-
-
How it's Generated:
-
Created by applying a strong electric field (AC, DC, pulsed, microwave, RF) to a gas (commonly air, oxygen, nitrogen, argon, helium, or mixtures) at atmospheric pressure or low pressure.
-
Common generation methods:
-
Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD): Electrodes separated by a dielectric barrier and a gas gap. Creates filamentary or diffuse plasma.
-
Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jet (APPJ): Gas flows through electrodes, generating a plume of plasma directed at a target.
-
Corona Discharge: High-voltage electrode with a sharp point creates plasma near the tip.
-
Capacitively or Inductively Coupled RF Plasma.
-
-
-
Key Components & Active Agents:
-
Energetic Electrons: Drive reactions.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Ozone (O₃), atomic oxygen (O), singlet oxygen (¹O₂), superoxide (O₂⁻), hydroxyl radicals (·OH).
-
Reactive Nitrogen Species (RNS): Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), peroxynitrite (ONOO⁻).
-
UV Photons: Emitted during relaxation of excited species.
-
Charged Particles (Ions & Electrons): Can interact with surfaces.
-
Electric Fields.
-
-
Why it's Powerful & Unique:
-
Low Temperature: Can treat heat-sensitive materials (plastics, biological tissues, food) without thermal damage.
-
Reactive Chemistry: The cocktail of ROS, RNS, UV, and ions can efficiently:
-
Kill microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, spores).
-
Modify surface properties (enhance wettability, adhesion, printability).
-
Degrade pollutants and toxins.
-
Promote specific chemical reactions.
-
Stimulate biological processes (e.g., wound healing, seed germination).
-
-
Dry Process: Often requires no liquids or harsh chemicals.
-
Fast & Efficient: Reactions typically occur rapidly.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Generally produces minimal waste compared to chemical methods; generated ozone/RNS decompose naturally.
-
-
Major Applications:
-
Sterilization & Decontamination: Medical instruments, packaging materials, hospital surfaces, food surfaces (fruits, vegetables, meat), water treatment, air purification.
-
Medicine (Plasma Medicine): Wound healing and disinfection (chronic wounds, burns), cancer therapy research, dentistry, skin treatment, blood coagulation.
-
Materials Processing & Surface Modification: Improving adhesion for paints/coatings/glues, enhancing textile dyeability, cleaning surfaces, creating functional coatings.
-
Food Industry: Extending shelf-life by killing pathogens and spoilage organisms on produce, meat, and packaging; seed germination enhancement; mycotoxin degradation.
-
Agriculture: Seed treatment for improved growth/resistance, plant disease control.
-
Environmental Remediation: Breaking down volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in air, degrading organic pollutants in water.
-
Electronics: Etching, deposition, cleaning wafers and components.
-
Energy: Fuel reforming, combustion enhancement.
-
In essence: Cold plasma technology harnesses the potent reactivity of a partially ionized gas at near-room temperature. It offers a versatile, efficient, and often eco-friendly alternative to traditional thermal, chemical, or radiation-based processes across diverse fields, particularly where heat sensitivity or chemical residues are major concerns. It's a rapidly advancing area of research and industrial application.

-400x400.jpg)
-400x400.jpg)
-400x400.jpg)
-400x400.jpg)